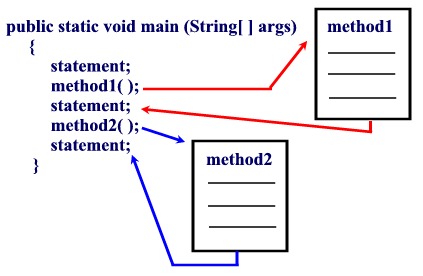
Think of a method as a subprogram that acts on data and often returns a value.
Each method has its own name. When that name is encountered in a program, the execution of the program branches to the body of that method. When the method is finished, execution returns to the area of the program code from which it was called, and the program continues on to the next line of code.
Methods are time savers, in that they allow for the repetition of sections of code without retyping the code. In addition, methods can be saved and utilized again and again in newly developed programs.
You are using methods when you use
System.out.print( ) and System.out.println( ).
There are two basic types of methods:
Built-in: Build-in methods are part of the compiler package, such as System.out.println( ) and System.exit(0).
User-defined: User-defined methods are created by you, the programmer. These methods take-on names that you assign to them and perform tasks that you create.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64