Processing Devices
CPU
The main chip in the computer is the central processing unit CPU. It is called the CPU because its main function is to process instructions, manage the flow of information through the computer system, and perform calculations. It is the heart of the computer and communicates with the output, input and storage devices to perform tasks that are important to the functioning of the computer.
The CPU is the brain of the computer. It carries out instructions given by user and manipulates data. There is a small amount of memory associated with CPU. It also uses the main memory.
CPU governs the overall speed of the computer. The speed of the CPU is measured in MHz ( Mega Hertz)
Motherboard
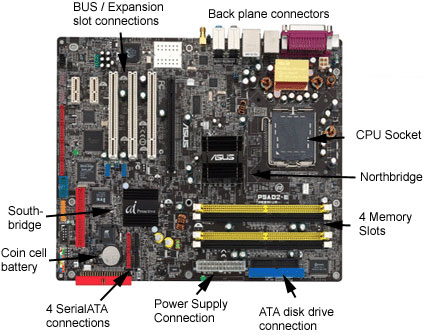
motherboard is the main circuit board in a computer system, which facilitates the connectivity of devices of the computer
It contains various sockets, slots, chips etc.
All the devices in a computer system connect to the motherboard. A device will be connected to the relevant port (which is on the casing of the system unit) and the port is connected with an expansion card. finally the expansion card (and or port) is connected to the motherboard.
The form factor refers to the standard specification of a motherboard which includes the size of the motherboard, the locations of various slots in the motherboard, slot sizes etc of the motherboard.
It contains various sockets, slots, chips etc.
All the devices in a computer system connect to the motherboard. A device will be connected to the relevant port (which is on the casing of the system unit) and the port is connected with an expansion card. finally the expansion card (and or port) is connected to the motherboard.
The form factor refers to the standard specification of a motherboard which includes the size of the motherboard, the locations of various slots in the motherboard, slot sizes etc of the motherboard.
System Bus
Bus refers to a collection of wires
A bus is used to carry signals between components
The bus is the communication path way between computer elements.
Bus refers to a collection of wires
A bus is used to carry signals between components
The bus is the communication path way between computer elements.
Processor bus:
This is the fastest bus in the computer system. This bus is used to pass information between the processor and cache or main memory.
PCI bus: This bus is used for high speed peripherals such as network card, video card and SCSI adapters. This bus is in the form of 32-bit slots (slots are explained below) mounted on the motherboard and is in white color. PCI-X and PCI-Express are more advanced versions of PCI.
ISA bus: This is a very slow speed bus and was used to connect slow speed devices such as modems and sound cards. This bus is now not included in modern systems.
AGP bus: This bus is used to connect the high speed video card.
This is the fastest bus in the computer system. This bus is used to pass information between the processor and cache or main memory.
PCI bus: This bus is used for high speed peripherals such as network card, video card and SCSI adapters. This bus is in the form of 32-bit slots (slots are explained below) mounted on the motherboard and is in white color. PCI-X and PCI-Express are more advanced versions of PCI.
ISA bus: This is a very slow speed bus and was used to connect slow speed devices such as modems and sound cards. This bus is now not included in modern systems.
AGP bus: This bus is used to connect the high speed video card.
Expansion Slots
Expansion cards are plugged into the Expansion slots.
Expansion slots are located in the motherboard. They are in different types such as PCI, ISA and AGP. They are connected to the system buses.
In a basic computer system you might not be able to perform all the tasks which you need. Therefore we need additional slots to plug in various expansion cards.
Can be fixed various expansion cards into these expansion slots. These additional expansion cards add more capability to the computer system.
Expansion cards are plugged into the Expansion slots.
Expansion slots are located in the motherboard. They are in different types such as PCI, ISA and AGP. They are connected to the system buses.
In a basic computer system you might not be able to perform all the tasks which you need. Therefore we need additional slots to plug in various expansion cards.
Can be fixed various expansion cards into these expansion slots. These additional expansion cards add more capability to the computer system.
This concept of expansion slots are needed because a basic computer system you buy might not be able to perform all the tasks which you need. So when you have a new requirement and need a new capability to be added to the computer system, what you do is plug in the relevant expansion card to the expansion slot and this adds a new feature to the computer system.
PCI
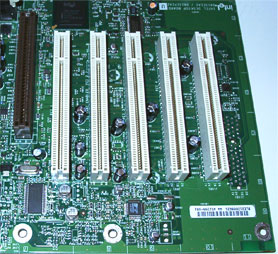
PCI was introduced to overcome problems of ISA and EISA.
PCI slots are used to connect high speed devices such as video cards, network cards, SCSI adapters etc...
These slots are on the motherboard and are in white colour. They are 32-bit slots.
PCI-X and PCI-Express are more advanced versions of PCI.

PCI was introduced to overcome problems of ISA and EISA.
PCI slots are used to connect high speed devices such as video cards, network cards, SCSI adapters etc...
These slots are on the motherboard and are in white colour. They are 32-bit slots.
PCI-X and PCI-Express are more advanced versions of PCI.
ISA
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) was introduced with an 8-bit bus in the orginal IBM PC in 1981. Later it was expanded to 16-bit.
These slots were connected to very slow speed bus. They were used to connect slow speed devices such as modems and sound cards.
ISA could handle a maximum of only 16-bits. But EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) could handle 32-bits. It is also compatible with ISA.
ISA cards can be plugged into the EISA. But in the modern systems ISA bus is unavailable.
ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) was introduced with an 8-bit bus in the orginal IBM PC in 1981. Later it was expanded to 16-bit.
These slots were connected to very slow speed bus. They were used to connect slow speed devices such as modems and sound cards.
ISA could handle a maximum of only 16-bits. But EISA (Extended Industry Standard Architecture) could handle 32-bits. It is also compatible with ISA.
ISA cards can be plugged into the EISA. But in the modern systems ISA bus is unavailable.
AGP
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is a standard created by Intel. The AGP connector looks similar to the PCI connector.
AGP slots are used to plug-in video cards. AGP bus is a high speed bus designed to be used for high-performance graphics and video support.
AGP base contains many differences compared to PCI. AGP slots are designed specifically to use with video cards.
AGP specifications were released by Intel:
AGP specification - AGP Version 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 8x.
AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) is a standard created by Intel. The AGP connector looks similar to the PCI connector.
AGP slots are used to plug-in video cards. AGP bus is a high speed bus designed to be used for high-performance graphics and video support.
AGP base contains many differences compared to PCI. AGP slots are designed specifically to use with video cards.
AGP specifications were released by Intel:
AGP specification - AGP Version 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 and 8x.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64