Number of new ideas and introduction of new technologies have contributed significantly to the development of computer. Some of the key developments are:
Abacus - calculating device (3000 BC) : Abacus is an ancient calculating device.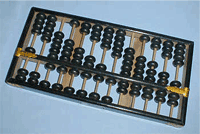 In the Abacus, small beads are arranged on a series of vertical rods in a manner that by manipulating them, it is possible with some skill and practice, to make rapid calculations. It is still being used in China, Russia and the Far East.
In the Abacus, small beads are arranged on a series of vertical rods in a manner that by manipulating them, it is possible with some skill and practice, to make rapid calculations. It is still being used in China, Russia and the Far East.
1614AD – Napier's bones John Napier (1550-1617), a Scottish mathematician, invented the Napier’s Bones - an aid to multiplication.
John Napier (1550-1617), a Scottish mathematician, invented the Napier’s Bones - an aid to multiplication.
A set of bones consisted of nine (9) rods, one for each digit 1 through 9. A rod is essentially one column of a multiplication table.
Pascaline-mechanical adding machine(1642) : 
 In 1642, Blaise Pascal, a French mathematician, invented Pascaline. Pascaline is a desktop mechanical adding machine.
In 1642, Blaise Pascal, a French mathematician, invented Pascaline. Pascaline is a desktop mechanical adding machine.
The machine has adopted partly the principles of the abacus but
did away with the use of the hand to move the beads or counters. Instead, Pascal used wheels to move counters.
Analytical Engine - by Babbage (1830s) :  Analytical Engine was invented by Charles Babbage who is known as “the father of computers”. Ada (1800s) was the world’s first computer programmer who collaborated with Charles Babbage.
Analytical Engine was invented by Charles Babbage who is known as “the father of computers”. Ada (1800s) was the world’s first computer programmer who collaborated with Charles Babbage.

 Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician who developed a mechanical tabulator based on punched cards in order to rapidly tabulate statistics from millions of pieces of data. It was electrically powered and used punched cards.
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 – November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician who developed a mechanical tabulator based on punched cards in order to rapidly tabulate statistics from millions of pieces of data. It was electrically powered and used punched cards. 
 Dr. Howard Aiken was a pioneer in computing, being the primary engineer behind IBM's Harvard Mark I computer.
Dr. Howard Aiken was a pioneer in computing, being the primary engineer behind IBM's Harvard Mark I computer.Mark I was invented by Dr. Howard Aiken. The idea is based on programmable, general purpose computer. Mark I was the first large-scale fully automatic digital computer that was very reliable.
• In 1937 John V. Atanasoff created the Atanasoff-Berry Computer (ABC). This is considered as the first electronic computer.
• In 1945 John von Neuman specified the architecture of the EDVAC, which introduced the stored-program computer concept.
• In 1946 John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert introduced the ENIAC, an electronic computing machine.
• In 1947 William Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen was successful in testing the point-contact transistor. This made the semiconductor revolution which helped to reduce the size of computers.
• In 1949 Maurice Wilkes at Cambridge University released the EDSAC, the first real stored-program computer.
• In 1952 UNIVAC I was developed and this is the first commercial computer which got a large amount of public attention.
• In 1953 IBM releases the IBM 701. This is IBMs first electronic computer.
• In 1955 Bell laboratories introduced the TRADIC, the first fully transistorized computer.
• In 1958 Jack Kilby at Texas Instruments created the first integrated circuit (IC).
• In 1969 the ARPAnet was developed. (This became the base for Internet later.)
• In 1971 IBM invented the 8” floppy disk.
• In 1972 Intel introduced the Intel 8008 microprocessor.
• In 1973 Robert Metcalfe introduced the Ethernet method for network connections.
• In 1974 Xerox Palo Alto Research Centre designed the first workstation with mouse input available.
• In 1977 Apple Computers introduced Apple II.
• In 1979 Motorola introduced the 68000 microprocessor.
• In 1980 Segate Technology created the first hard disk drive for microcomputers.
• In 1981 Xerox introduced the Star, the first personal computer with a graphical user interface (GUI).
• In 1981 Sony introduced the 3 1/2” floppy drives.
• In 1982 Sony introduced the first CD player.
• In 1984 Apple Computer introduced the Macintosh, the first successful mouse driven, GUI based computer.
• In 1984 IBM released the personal computer PC-AT. This introduced the 16-bit ISA bus and is the computer which all modern personal computers are based.
• In 1985 Philips introduced the first CD-ROM drive.
• In 1987 IBM introduced its PS/2 machines. This machine made the 3 1/2” floppy disk drives and VGA video standards for personal computers.
• In 1988 EISA architecture was developed.
• In 1995 Microsoft introduced the Windows 95 operating system. This is the first main 32-bit operating system.
• In 1997 Intel released the Pentium II microprocessor.
• In 1997 AMD released the K6 microprocessor.
• In 1998 Microsoft released Windows 98.
• In 1999 Intel released the Pentium III, with SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions) added.
• In 1999 AMD released Athlon.
• In 2000 Microsoft released Windows Me and Windows 2000.
• In 2000 both Intel and AMD released processor at 1 GHz.
• In 2000 Intel released Pentium 4. It belongs to Intel Architecture 32-bit (IA-32) family.
• In 2001 Intel released the Itanium processor. This is Intel’s 64-bit processor for personal computers.
• In 2001 Microsoft released Windows XP.
• In 2002 Intel released the Pentium 4 with 3GHz speed. This processor also included the Hyper-Threading (HT) technology.
• In 2003 Intel released the Pentium M, a processor designed for mobile computer systems.
• In 2005 Intel released the dual core processor named Core Duo
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64