| Life Processes and Cell Activities The 7 life processes are what all living organisms do. You must learn these for the exam. A good way of doing this is remembering the phrase "Mrs Gren"
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cells | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
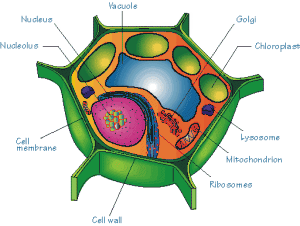
| Differences Between the Animal and Plant Cells | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells. They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Both also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal elements. The functions of these organelles are extremely similar between the two classes of cells (peroxisomes perform additional complex functions in plant cells having to do with cellular respiration). However, the few differences that exist between plant and animals are very significant and reflect a difference in the functions of each cell.Structurally, plant and animal cells are very similar because they are both eukaryotic cells. They both contain membrane-bound organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and peroxisomes. Both also contain similar membranes, cytosol, and cytoskeletal elements. The functions of these organelles are extremely similar between the two classes of cells (peroxisomes perform additional complex functions in plant cells having to do with cellular respiration). However, the few differences that exist between plant and animals are very significant and reflect a difference in the functions of each cell. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Tissues - Made up of lots of cells of the same type. (e.g. muscle tissue is made up of many muscle cells) Tissues - Made up of lots of cells of the same type. (e.g. muscle tissue is made up of many muscle cells)Organs - Different tissues working together to carry out a certain function. An organ can contain different types of tissue (e.g. the heart). Organ Systems - Organ systems are composed of two or more different organs that work together to provide a common function. |
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64