Large or Diffuse Light Sources
- ආලොක කිරණ අපසාරී හෙවත් විසිරී යයි, සමාන්තර නොවේ.
- හොඳින් පෙනෙන දැකුම් වෘත්තයක් තිබේ.
- එක මත වැටෙන ද්වි සෙවනැලි සෑදේ.
- එයට සූර්ය ආලෝකය හෝ එහි පරාවර්ථන බලපෑම් ඇතිවිය හැක. සංකීර්ණ සෙවනැලි ඇතිකරයි.
- තද අඳුරු සෙවනැලි අරටුවක් තිබේ.
- මෙහිදී ප්රභවය සංකීර්ණ විසුරුම් ජනේලයක් සාදයි.
- විසුරුම් ජනේලයේ වටය හා අඳුරු අරටුව ලබා ගැනීමට ජ්යාමිතිය භාවිතා කළ හැක.
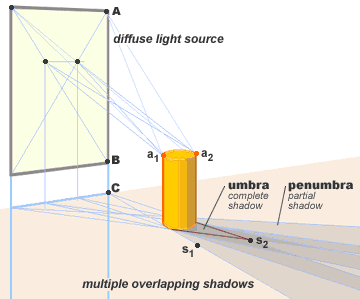
මේ ජනෙල් කවුළුවකින් වැටෙන ආලෝකයෙන් ජනිත වන සෙවනැල්ලකි.
- A in the window and points, a1 and a2 on cylinder.
- A, a1, a2 cast two shadow points, s1 and s2, on the horizontal surface.
- Point A is the light vanishing point
- point C is on the horizontal plane directly below A
- C is the vertical shadow vanishing point (svp [vertical]).
The penumbra
The umbra
All diffuse cast shadows can be solved in a similar way, first by plotting the extreme outside edges of the shadow from the extreme top, side and bottom points of the large light source, which will show the boundaries of the penumbra and umbra, then gradating the difference between the umbral and penumbral values from the edge of the umbra out to the edge of the penumbra.
The amount of lightness contrast between the diffuse shadow and the illuminated part of the horizontal surface depends on the total amount of light coming from the diffuse light source (the window), the proportion of light coming from other sources in the room, including reflected light from the walls and ceilings, and the light adaptation of the eye.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64