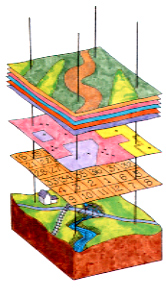
The GIS assists people in analyzing data and making informed decisions concerning different resources—such as wildlife, minerals, plant, hydrology, and soil. entered into GIS, can look across disciplines and see the "big picture."
GIS technology is used by resource managers for a number of purposes such as determining suitability of an area for wildlife habitat, mapping areas at risk for fire, or assessing the health of rangelands and riparian areas in order to manage grazing practices.
Another advantage to GIS is its ability to show changes in information over time. Data can be collected from even antiquated sources. Trends can be projected into the future as well.
(1) To store and manage geographic information comprehensively and effectively
(2) To display geographic information depending on the purpose of use
(3) To execute query, analysis and evaluation of geographic information effectively
GIS and Remote Sensing
In order to promote the integration of remote sensing and geographic data, geographic information system (GIS) should be established in which both the image and graphic data are stored in a digital form, retrieved conditionally, overlaid on each other and evaluated with the use of a model.
(1) Model and data structure for GIS
(2) Data input and edition
(3) Spatial query
(4) Spatial analysis
(5) Visualization
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64