SQL JOIN combine rows from two or more tables, based on a common field between them.
Customers Table
CustomerID CustomerName ContactName Country 1 Alfa System Mary Muller Germany 2 Analtics Cray Ana Turilo Mexico 3 Antonio Trading Antonio Mori Mexico
Orders table
OrderID CustomerID OrderDate 10308 2 2015-09-18 10309 37 2015-09-19 10310 77 2015-09-20
Relationship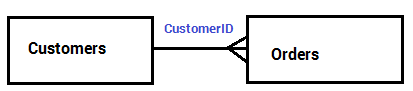
Notice that the "CustomerID" column in the "Orders" table refers to the "CustomerID" in the "Customers" table. The relationship between the two tables made with the "CustomerID" column/field.
INNER JOIN SQL Statement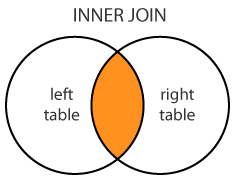
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customers
ON Orders.CustomerID=Customers.CustomerID;
IMPORTANT POINTS
- A SQL JOIN combines records from two tables.
- A JOIN locates related column values in the two tables.
- A query can contain zero, one, or multiple JOIN operations.
- INNER JOIN is the same as JOIN; the keyword INNER is optional.
Different types of JOINs
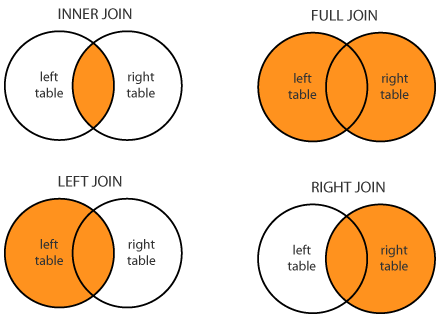
LEFT JOIN
returns all the rows from the left table (Customers), even if there are no matches in the right table (Orders)
SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID
FROM Customers
LEFT JOIN Orders
ON Customers.CustomerID=Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CustomerName;
RIGHT JOIN
The RIGHT JOIN keyword returns all the rows from the right table (Employees), even if there are no matches in the left table (Orders).
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Employees.FirstName
FROM Orders
RIGHT JOIN Employees
ON Orders.EmployeeID=Employees.EmployeeID
ORDER BY Orders.OrderID;
FULL OUTER JOIN
returns all the rows from the left table (Customers), and all the rows from the right table (Orders). If there are rows in "Customers" that do not have matches in "Orders", or if there are rows in "Orders" that do not have matches in "Customers", those rows will be listed as well.
SELECT Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderID
FROM Customers
FULL OUTER JOIN Orders
ON Customers.CustomerID=Orders.CustomerID
ORDER BY Customers.CustomerName;
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64