What is a database ?
A database is an organized collection of information for easy access, management, and update.
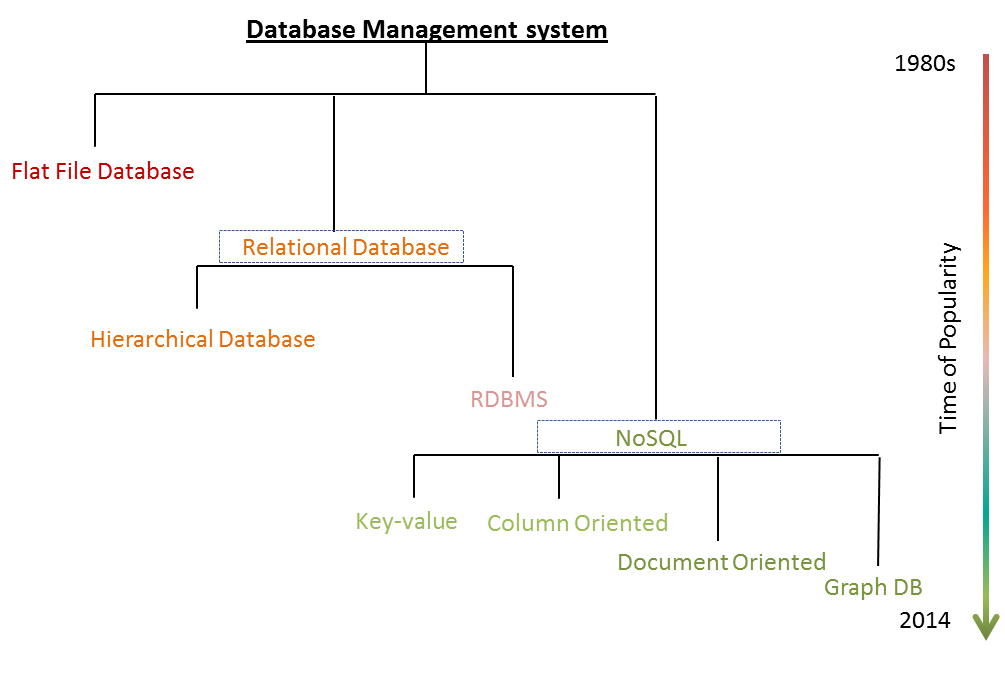
Types of Database Systems
- Flat file system
- Hierarchical Model
- Network Model
- Relational Model
- Object Relational Model
- No SQL Data model
Flat file database
- The data stored in a ordinary "flat file". (names.txt)
- Example: contact list.
- The whole file need to be read to read and process data.
- Takes longer time to read large sets of data.
- Data limited by memory size.
- Good for small amount of data
Hierarchical Database
Similer to the folder structure on a computer.
Every folder can contain a sub-folder and each sub-folder can still hold more sub-folders. Finally, in some folders, we will store files. Every child node (sub-folder) will have a single parent (folder or sub-folder). This creates a hierarchy of the dataset.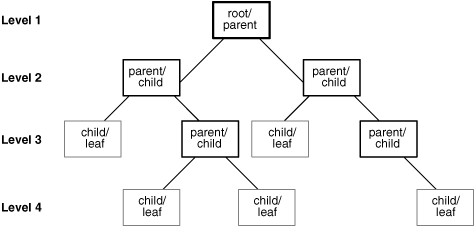
Object-oriented Database
- The Object and its data accessed through pointers.
- Support diverse structures and extendable.
- The data and the program operate as one.
- This model treat the data as native code.
Relational Database Systems
Most widely used . Easy to use.
Data stored in rows and columns in tables.
The data have relationships with other tables (Class > Students > Subjects > Marks)
Data stored is fixed predefined structures . Many empty spaces
Data manipulated using Structured Query Language (SQL).
Examples:
Dbase III+, MS Access, Oracle, Ms SQL Server, mySQL , IBM DB2, SQLite, and PostgreSQL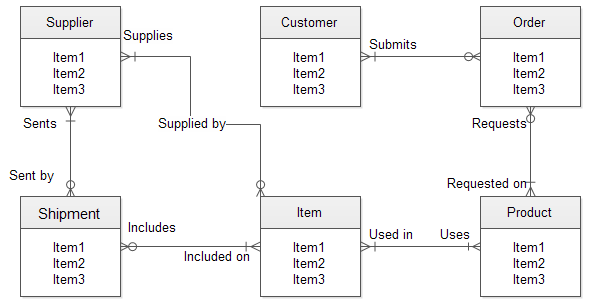
No SQL Database
Keeps data in key = value pairs.
Highly flexible structure
Scalable
Facebook stores terabytes of additional data every day using no SQL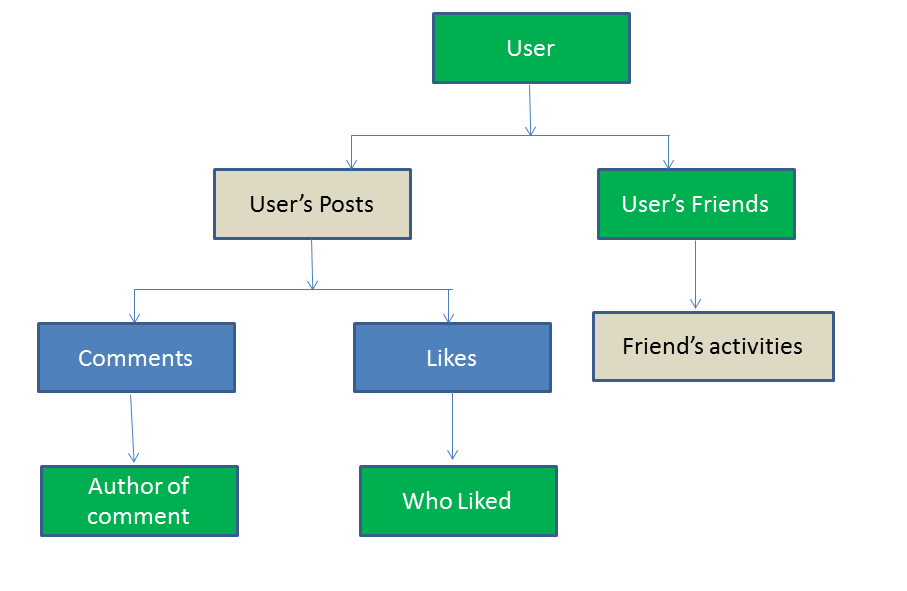
Ex. Mongo DB
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64