Check the following IP addresses and find if they are correct.
1. Identify Class of IP Address
2. Check the Address Range
3. Check Network ID or Host ID format.
4. Check network id or host id not accepted
245.12.33.102 (245 is Experimental)
123.123.123.123
199.23.107.255 (Host ID bits cant be all 1s=255=11111111 )
199.23.107.0 (Host ID is 0 cant be)
156.266.12.103 (266 is invalid number)
153.0.0.0 (Host ID bits are all 0 = 00000000 )
153.0.0.255
191.23.255.255
33.255.255.1
12.0.0.0
12.255.255.255
12.0.0.255
127.0.0.1 (127 is the reserved “loopback address”)
127.23.109.122
0.23.12.122
192.12.255.102
191.105.0.0
203.123.45.255
204.0.23.198
224.56.204.112 (224 is a multicast address, cannot be used with hosts)
126.0.0.1
177.45.123.255
Network ID Guidelines
- The network ID identifies a physical segment of the network.
- All hosts on the same physical network assigned the same network ID to communicate with each other.
- The network ID must be unique to the IP network.
- The network ID must be unique to the Internet.
- The network ID cannot begin with the number 127.
- The number 127 is a class A address is reserved for internal loopback functions.
- All bits within the network ID cannot be set to 1 (11111111). All 1's (255) in the network ID are reserved for use as an IP broadcast address.
- All bits within the network ID cannot be set to 0 (00000000). All 0's (0) in the network ID are used to denote a specific host on the local network and are not routed.
Host ID Guidelines
- The host ID identifies a device within a network.
- The combination network ID + host ID is an IP address.
- The host ID is unique to the network ID.
- All bits within the host ID cannot be set to 1 (11111111) - because this host ID (255) is reserved as a broadcast address to send a packet to all hosts on a network.
- All bits in the host ID cannot be set to 0 (00000000) because this host ID (0) is reserved to denote the network ID.
Public and Private Addresses
If your intranet is not connected to the Internet, any IP address can be used.
If connectivity to the Internet is needed, there are two types of addresses used on the Internet.
Public Addresses
Public addresses are assigned by InterNIC and consist of class-based network IDs globally unique to the Internet.
Private Addresses
Each device connecting to a network uses an IP address that is unique to the network. In the Internet, each host connecting requires a globally unique IP address. As the Internet grew, organizations required a public address for hosts on their intranets. To solve this addressing problem, a portion of the IP address space reserved. An IP address in the private address space is never assigned as a public address.
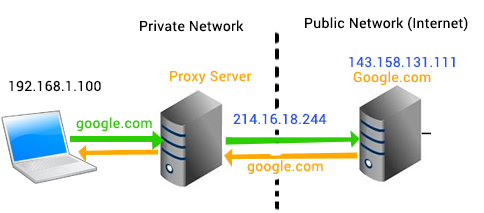
Private addresses are not reachable on the Internet. Therefore, Internet traffic from a private address sends its requests to the gateway (proxy server), with a valid public address.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64