In this diagram we find two Network Segments.
Segment 1 has IPs 192.168.1.0 - 192.168.1.24
Segment 2 has IPs 10.20.0.0 - 10.20.0.24
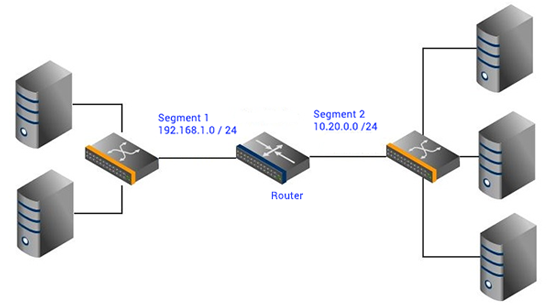
- The data broadcast by segment 1 not received by segment 2.
- Segment 2 has 3 hosts receive broadcasts from each other.
- Segment broadcasts Ignore repeaters, bridges, and switches.
- The switch in segment forward broadcasts to hosts in the same segment.
- Segments exist behind a port of a router and between routers
- Routers only forward IP packets addressed to other networks/hosts.
IP address has two main parts.
Network ID
The network Id is common for all computers of a physical network segment
Its unique in the entire network. All hosts in the network share one network ID.
Network IS is like the postal code of your address. Many people in the city share it.
HOST ID
Host id is unique to each device/host in a network.
Host ID is like your house number. Only one of such numbers exists in the city.
When we route a packet Network ID tells which network to forward the packet.
Once received by switch uses host ID to submit the packet.
The IP addressing rules
- Each physical network segment has a unique Network ID
- All devices on the same physical segment share the same network ID
- Each device on the same physical segment has a unique host ID
IPV4 Address Classes
The Internet defines five address classes to accommodate networks of varying sizes.
Each class defines network ID and host ID with a specific number of bits.
Each class also defines a possible number of networks and the number of hosts per network.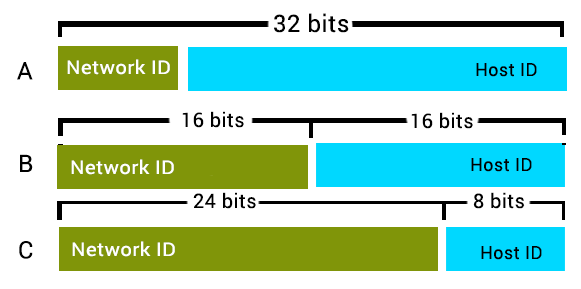
Addresses available in each class
Class A : 1.0.0.0 - 127.255.255.255
Class B : 128.0.0.0 - 191.255.255.255
Class C : 192.0.0.0 - 223.255.255.255
Class D : 224.0.0.0 - 240.255.255.255 (Multicast - Not used for host addressing)
Class E : 241.0.0.0 - 255.255.255.255 (Experimental -Not used for host addressing)
Network Class of an IP can be easily identified from first number (8 bits).
Class A (0 -127), Class B (128 - 191), Class C (192-223) , Class D (224 - 240) etc.
Class A
Class A addresses are assigned to networks with a very large number of hosts.
Class A allows 126 networks and 16,777,214 hosts per network.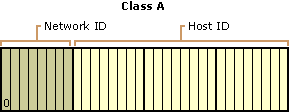
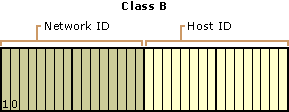
Class B
Class B addresses are assigned to medium-sized to large-sized networks. This allows for 16,384 networks and 65,534 hosts per network.
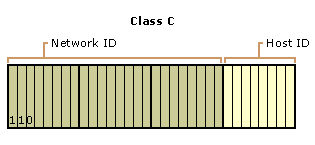
Class C
Class C addresses are used for small networks.
This allows for 2,097,152 networks and 254 hosts per network.
Class D
Class D addresses are reserved for IP multicast addresses.
Class E
Class E is an experimental address that is reserved for future use.
Summery
1.0.0.0 - 126.255.0.0
How ever 1st and last address not used.
Class A (1-126) Network.host.host.host
127 is used as loopback address 127.0.0.0/8
Class B (128-191)
Class C (192-223)
Class D (224-223)
Class E (240-254)
The first and last numbers of network address ranges are not used.
Example : In Class A - 0 and 127 are not used.
Usable Network addresses
A : 1.0.0.0 - 126.255.0.0
B : 128.0.0.0 - 191.255.255.0
C : 192.0.0.0 - 239.255.255.0
Identify Network Class of following IPs
Tip : Look at the first number . 0-127 is A, 28-191 are B, 192-223 are C
210.23.67.102
66.23.148.0
158.23.251.33
144.23.117.254
192.254.23.123
144.207.78.1
63.125.23.211
192.25.128.36
128.12.254.98
134.223.156.89
127.0.0.1
224.23.108.23
223.78.27.144
77.123.28.167
191.249.222.234
19.23.12.255
188.67.76.235
134.255.123.22
143.52.213.212
207.22.45.219
117.117.117.117
193.23.255.77
199.23.255.7
145.2.229.252
238.23.177.8
Find Network ID or Host ID
Tip : Identify class first and then check network id and host ID
Class A format is Network.host.host.host
Class B format is Network.Network..host.host
Class C format is Network.Network.Network.host
Find Network ID : 1.102.45.177
Find Host ID : 196.22.177.13
Find Network ID : 133.156.55.102
Find Host ID : 221.252.77.10
Find Network ID : 123.12.45.77
Find Host ID : 126.252.77.103
Find Network ID : 13.1.255.102
Find Host ID : 171.242.177.109
Find Network ID : 193.156.155.192
Find Host ID : 21.52.177.188
Find Network ID : 77.77.45.77
Find Network Class, Network ID and Host ID
191.252.77.13
191.15.155.2
221.252.117.254
203.10.233.1
191.2.227.19
23.156.1.92
121.2.199.88
202.27.189.177
177.222.177.28
198.215.67.233
128.252.17.24
212.199.19.29
159.255.17.218
155.25.169.133
191.255.217.227
Loop-back address (Localhost)
IPv4 reserve the entire 127.* address block for loop-back purposes. That means any packet sent any of 16,777,214 addresses (127.0.0.1-127.255.255.254) is looped back. IPv6 has just a single address, ::1.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64