IP addresses are logical addresses used to uniquely identify devices on a computer network.
- IP address is a numerical label assigned to each device.
- IP addresses are used by to communicate using Internet Protocol (IP).
The switch connecting devices, maps/translates the physical address to the logical IP address, when the device connects.
The IPV4 addressing scheme.
IPV4 uses 32-bit addressing scheme
Every 8 bits is a number between 0 and 255.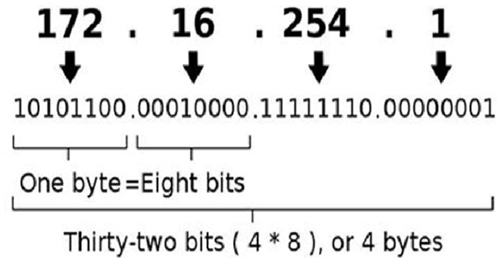
Logically we can create 256 x 256 x 256 x 256 addresses from
0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. However, not all addresses are used for hosts.
0 and 255 are special numbers used for the network address and broadcast address.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) manages the IP address space allocations globally. IANA has delegated five Regional Internet registries (RIRs) to allocate of IP address blocks to local Internet registries (Internet service providers) and other entities like web hosting companies.
If shilpasayura.net is hosted in a web server having 168. 150.111.234 IP address.
The name shilpasayura.net indicates what we seek.
An address 168. 150.111.234 indicates where it is.
A route indicates how to get there.
The DNS resolves the shilpasayura.net domain name to its IP 168. 150.111.234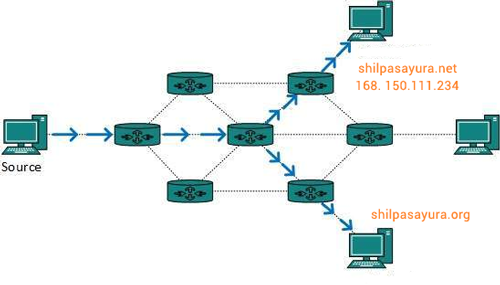
IPV6 addressing/
The IPV4 address range is not adequate to assign for all devices connecting to the internet. With iOT like devices increase the demand for IPs. Hence a new version of IP addressing was introduced as (IPv6). IPV6 uses 128 bits for the address.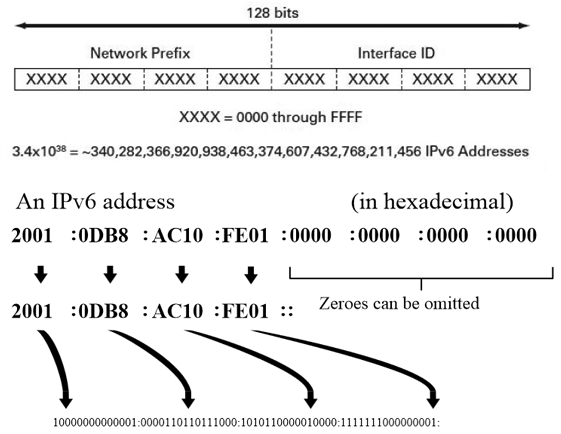
What is a Physical Network Segment?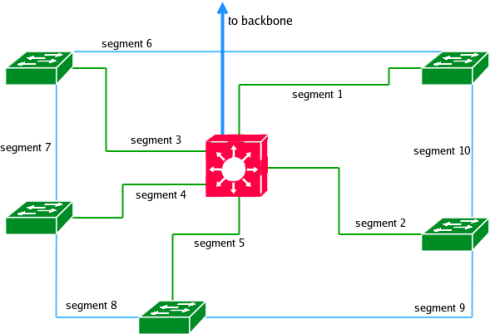
-A physical network segment is a broadcast domain. Data broadcasted on the segment is received by all devices in the segment.
-It Ignore repeaters, bridges or switches
-It forward broadcasts
-It is behind a port of a router
-Segment exist between routers
-routers don’t forward broadcasts. They route packets addressed for other networks.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64