A wide range of devices are used for networking.
- Repeaters - Increase Signal Strength (Amplify)
- Regenerators - Correct the amplitude levels and transmits
- Hubs - Connect network devices to send and recieve data packets/frames
- Switches - Intelligent packets/frames forwaring in a network
- Bridges - Connect different networks (speed, topology and protocols)
- Routers - Connect LAN to a wide area network with logical addressing
- Gateways - connect networks using different protocols.
- CSU/DSU - handshaking and error correction to maintain a connection
- Network interface cards (NICs) - Connect Computer/Device to a Network
- Wireless access points (WAPs) - Provides Wireless LAN connctivity
- Modems - Convert Digital Signals to Analog and transmit and Vice Versa
HUB - central point for the devices to connect.
- Has multiple, independent ports that match the cable type .
- Support Category 3 or 5 twisted-pair cable with RJ-45 ends,
- Coax BNC and Fiber Optic BNC hubs also exist.
- Inexpensive option for transporting data between devices
- Hubs don't offer any form of intelligence.
- An active hub strengthens and regenerates the incoming signals before sending the data on to its destination.
- Passive hubs do nothing with the signal.
Switches
- A special type of hub with intelligent packet forwarding.
- A switch read the MAC address of each frame it receives and forwards only to the computer a frame is addressed.
- Speeds up the network and reduces congestion.
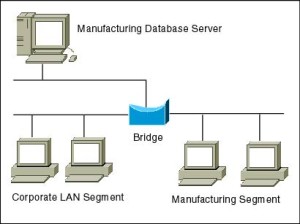
Bridges
- A bridge is used to join two network segments together.
- Used to divide large networks into smaller segments.
- Bridges can connect networks that run at different topologies, speeds and protocols.
- Bridges read the MAC header of each frame to determine on which side of the bridge the destination device is located, then transmits the packer to the segment where the device is located.
Routers
- Routers forwardpackets from one logical network to another.
- Routers are used in large internetworks to move packets between logical addresses.
- Routers have better packet-routing and filtering capabilities than bridges.
Routing tables
Routers contain internal table that keep track of all known network addresses and possible paths throughout the internetwork
Routers route packets based on the available paths and their costs.
The routing tables are the heart of a router; without them, there's no way for the router to know where to send the packets it receives.
Gateways
A gateway is used to connect networks using different protocols.
Gateways receive data from a network using one type of protocol stack, removes that protocol stack and repackages it with the protocol stack that the other network can use.
Examples
E-mail gateways - Translates SMTP into a standard X.400 format, and forwards it to its destination
Microsoft SNA Server
X.25 packet-switching network
CSU / DSU (Channel Service Unit / Data Service Unit)
A CSU/DSU used to connect a LAN to a WAN
A DSU provides all the handshaking and error correction required to maintain a connection across a wide area link, similar to a modem.
The DSU will accept a serial data stream from a device on the LAN and translate this into a useable data stream for the digital WAN network.
Network Interface Card (NIC)
NIC is a hardware card installed in a computer so it can communicate on a network.
NIC Functions
Data encapsulation
Building the frame for data and pass to the network layer.
Signal encoding and decoding
Converts the binary data in the frame-into electrical voltages or light pulses for the medium and vice versa.
Transmission and reception
Generate and transmit signals and receive incoming signals.
NIC examines the destination address in each packet, to see if it is intended for that computer. If so, the network interface adapter passes the packet to the computer for processing by the next layer in the protocol stack; if not, the network interface adapter discards the packet.
Data buffering
Network interface adapters transmit and receive data one frame at a time, so they have built-in buffers that enable them to store data arriving either from the computer or from the network until a frame is complete and ready for processing.
Serial/parallel conversion
The computer and NIC runs in parallel, either on 16 or 32 bits at a time, depending on the bus.
Network communications are serial running one bit at a time. The NIC performing the serial to parallel conversion .
Media access control
NIC implements the MAC mechanism to regulate access to the network medium.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64