The signal received will differ from signal transmitted due to Distortion, Attenuation and Noise called Transmission impairments.
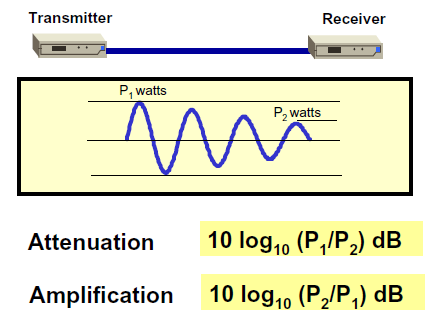
Attenuation
Reduction in the strength of a signal.
Attenuation occurs in both digital or analog signals.
Attenuation (loss) is a natural consequence of transmission over long distances.
The signal is amplified to solve this problem.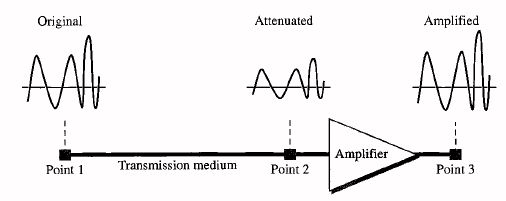
CCTV Signal Amplifier
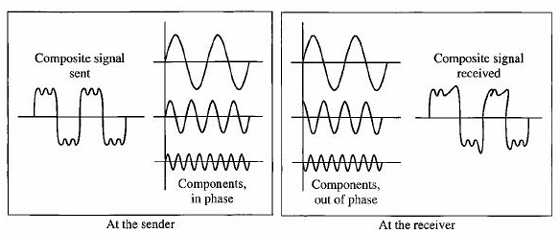
Distortion
Distortion is an undesired change in an electric signal waveform passing from the input to the output of a device.
- Distortion results in poor audio transmission passing through electronic devices
- The amplitude of an input signal may be changed.
- Frequency distortion occurs when the amplitudes of the frequencies change.
- Phase distortion occurs when there is a phase shift between output and input.
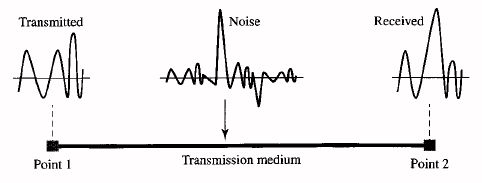
Noise
Noce is unwanted electromagnetic energy that degrades the quality of signals and data. Noise occurs in digital and analog systems.In a hard-wired circuit such as telephone lines, external noise is picked up from electrical transformers and the atmosphere. During severe thunderstorms, external noise can affect communications.
Noise is a problem in wireless systems than in wired systems. Noise can be minimized with digital signal processing and using fiber optics.
Signal-to-Noise-Ratio:
The Signal-to-Noise-Ratio is defined as average signal power is divided by the average noise.
Sources of errors and ways to minimize them
| Source of Error | What Causes It | How to Prevent It |
| Line outages | Storms, accidents | |
| White noise | Movement of electrons | Increase signal strength |
| Impulse noise | Sudden increases in electricity (e.g., lightning) | Shield or move the wires |
| Cross-talk | Multiplexer guardbands too small or wires too close together | Increase the guardbands or move or shield the wires |
| Echo | Poor connections | Fix the connections or tune equipment |
| Attenuation | Gradual decrease in signal over distance | Use repeaters or amplifiers |
| Intermodulation noise | Signals from several circuits combine | Move or shield the wires |
| Jitter | Analog signals change phase | Tune equipment |
| Harmonic distortion | Amplifier changes phase | Tune equipment |
Line noise and distortion can cause data communication errors. The focus in this section is on electrical media such as twisted-pair wire and coaxial cable, because they are more likely to suffer from noise than optical media such as fiber-optic cable.
White noise or Gaussian noise (the familiar background hiss or static on radios and telephones) is caused by the thermal agitation of electrons and therefore is inescapable.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64