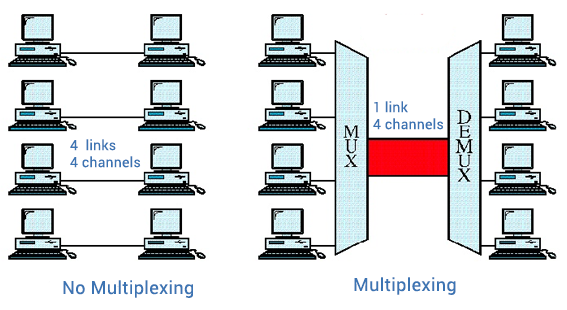
Need for multiplexing
multiplexing is used to transmit multiple signals over a shared medium.
In electronics, several analog signals are processed by one analog-to-digital converter (ADC).
In telecommunications, several phone calls are transferred using one wire.
Multiplexed divides the capacity of the communication channel into several logical channels. The reverse process is demultiplexing, extracting the original channels on the receiver side.
Multiplexing
Reduce network costs by minimizing the number of communications links needed between two points.
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)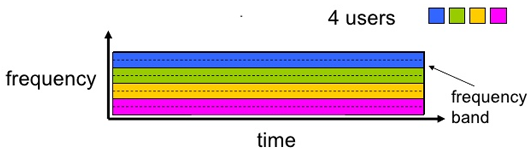
- FDM divides the Bandwidth available into smaller individual bands or channels
- FDM assigns a different frequency to each user/port/device.
- The signals travel parallel over the same communications link divided by frequencies.
- FDM used extensively in cable TV and in radio
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)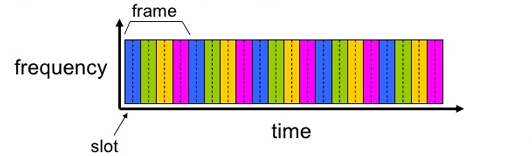
TDM assigns a time slot for each port in frame for separating individual channels.

TDM is more efficient than FDM because more subchannels can be created.
When one port is communicating the others are waiting hence wasting bandwidth when vacant slots occur on idle stations.
FDM and TDM can be combined. We can use FDM to create channels and then within each channel apply TDM to carry multiple conversations of the channel. GSM uses this method.
Synchronized TDM
A slot in each frame allocated to a port. if there is no data in the port empty slot sent.
Asynchronous TDM
Each frame has a message and index of which device (port) to receive the message.
The length of time allocated is not fixed for each device.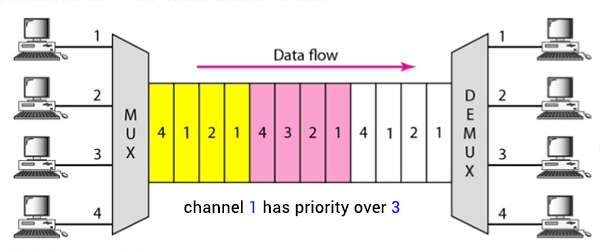
Code division multiplexing (CDM)
CDM allow multiple users to share a single communications channel.
- CDM combines multiple data signals for simultaneous transmission over a common frequency band.
- The data signal is sent over a range of frequencies .
- A random code is used to multiplex the base signal. The receiving device is aware of the random code and uses it to demultiplex the signal.
- CDM provide privacy and security of communications.
- CDM is used in 2G, 3G and 4G mobile phone technology.
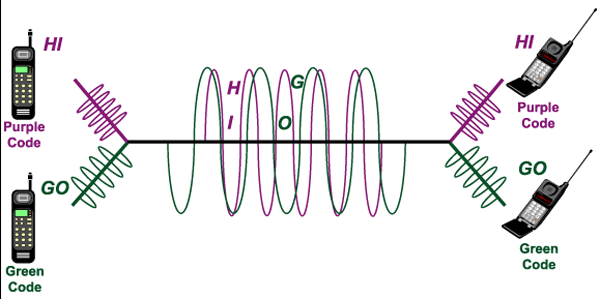
CDMA ("spread spectrum") is a form of multiplexing where the transmitter encodes the signal using a random sequence which the receiver also knows and can use to decode the received signal. Each different random sequence corresponds to a different communication channel.
Compare Frequency Allocation in FDM, TDM and CDM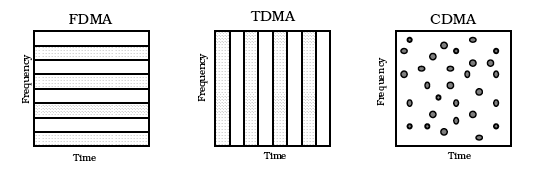
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM)
Light has different wavelength (colors). In fiber optics, multiple optical carrier signals (light) are multiplexed into an optical fiber by using different wavelengths.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64