MODEM (modulator-demodulator)
A modem is used to send digital data over a phone line.
The sending modem modulates the data into a signal that is compatible with the phone line, and the receiving modem demodulates the signal back into digital data. Wireless modems convert digital data into radio signals and back.

- Modem encodes Digital Signals to Analog transmission (Modulation) and decodes Analog transmission (Demodulation) to digital signals.
- Modem transmits digital data of a computer as a modulated electrical signal for transmission over telephone lines and demodulated by another modem at the receiver side to recover the digital data.
Computer Connecting to internet is an example using a modem.
56K Modem Card
Modem speed measured in bits per second (bps).
Modem symbol rate is measured in baud or symbols per second, or the number of times per second the modem sends a new signal.
ADSL (asymmetric digital subscriber line)
ADSL modems use a range of radio frequencies to carry radio and television signals and broadband internet service without interference.
ADSM Modems use quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM)
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
The standard technique for routing these packets through modems is called the Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP). Your computer's TCP/IP stack forms its TCP/IP datagrams and is handed over to the modem for transmission. The ISP receives each datagram and routes it appropriately into the Internet. The same process occurs to get data from the ISP to your computer.
Cable Modem Circuit Diagram
Observe Downstream and Upstream circuits for modulation and demodulation.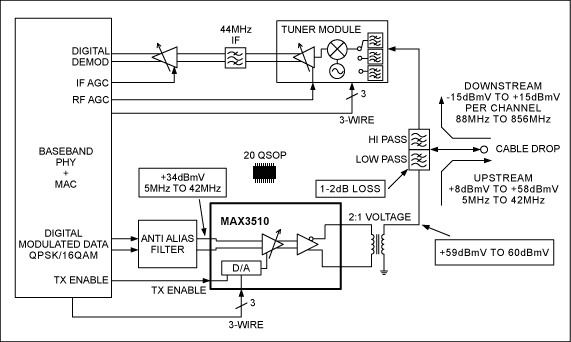
Modems through years (Brief history of modems)
ADSL Modem
ADSL Cabling System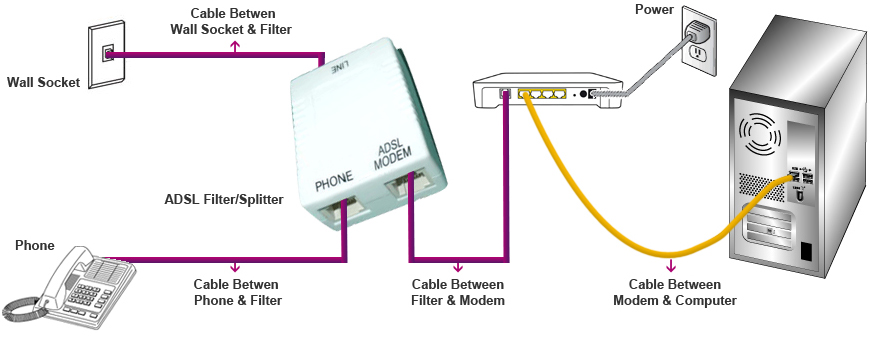
ADSL Wireless Lan Modem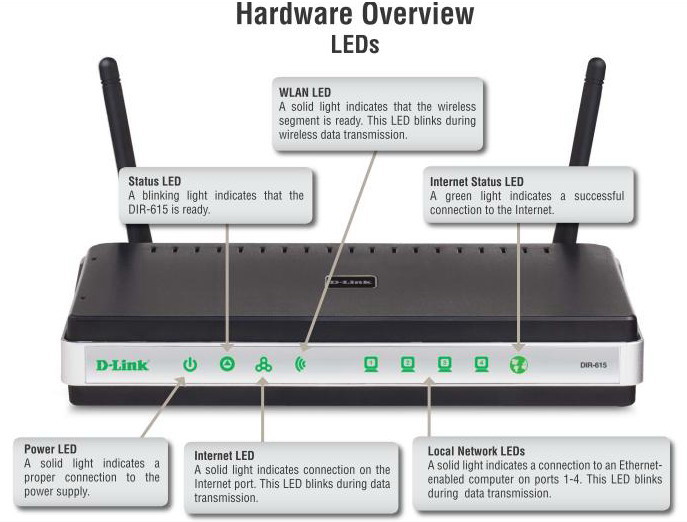
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64