Data transmission and Reception
When we speak to a microphone, our voice produces a series of compressions and refractions. A microphone acts as a transducer to convert these parameters into their corresponding varying current value. Since the signal strength of audio frequency is less, it has to be amplified to strengthen the signal before sending it over long distances. A strong carrier wave is used for this purpose.
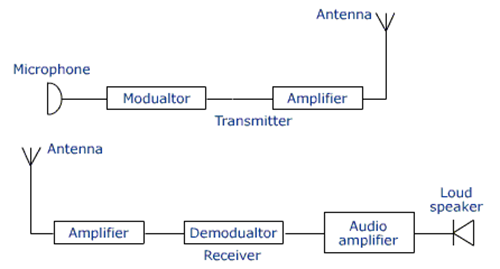
The resulting modulated wave is radiated out of the transmitter antenna and travels through space till it reaches the receiver antenna. The receiving aerial consists of a receiver that separates both the carrier signal and audio-frequency signal. The process of the receiver by which the audio frequency is separated from the carrier signal is called demodulation. The demodulated audio signal is sent to the loudspeakers for the user to hear.
Carrier Signal
Carrier signal is an electromagnetic pulse or wave transmitted at a steady base frequency used to carry a signal. The carrier increases signal strength. The carrier signal is modulated by varying the base frequency or other means.
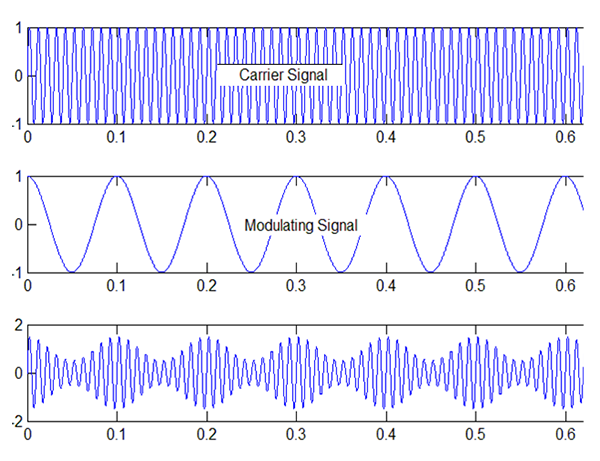
Amplitude Modulation (AM)
Variation of the amplitude of the high-frequency carrier wave .
AM keeps the carrier frequency unchanged. The input signal is superimposed on the carrier wave.
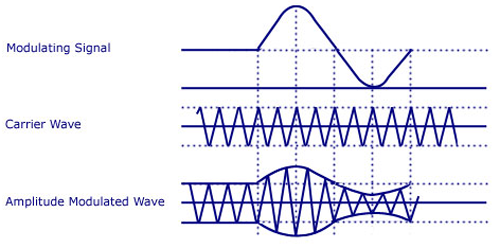
Limitations of Amplitude Modulation
- Low Efficiency- Due to small bands, the efficiency of AM is low.
- Limited Operating Range The range of operation is small due to low efficiency.
- Noise in Reception difficult for the receiver to distinguish amplitude variations, hence heavy noise can occur.
- Poor Audio Quality – interference from the adjacent broadcasting stations.
Frequency Modulation
FM is widely used radio communications. FM modulates the frequency of the carrier signal with the transmit signal.The frequency of the transmitted signal varies as the voltage of the modulating signal changes.
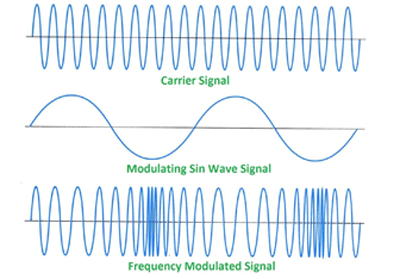
Frequency modulation is used in a wide variety of radio communications applications
Ex. Radio Broadcasting, Two-way radio communications links , Mobile radio communications. FM has many advantages over amplitude modulation (AM).
Advantages of FM
Resilient to noise
Resilient to signal strength variations
Disadvantages of FM
Requires more complicated demodulator
Filters used introduce some distortion of the signal.
Phase modulation (PM)
PM impressing data onto an alternating-current (AC) waveform by varying the phase of the wave. This method can be used with analog or digital data.

In analog, the phase of the carrier varied gives infinite carrier phase states. Based on the polarity of the input waveform, the carrier phase shifts in one direction and the opposite direction. At every instant in time, the extent of carrier-phase shift (the phase angle) is proportional to the signal amplitude.
In digital PM, the carrier phase shifts abruptly, rather than continuously back and forth. The number of possible carrier phase states is usually a power of 2. If there are only two possible phase states, the mode is called bi-phase modulation. In more complex modes, there can be four, eight, or more different phase states. Each phase angle represents a specific digital input state.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64