CDMA (Code-Division Multiple Access)
CDMA is a form of multiplexing used in second-generation (2G) and third-generation (3G) wireless communications. It allows many signals to occupy a single transmission channel. CDMA optimizes the use of bandwidth and enhances communication privacy making cloning difficult. CDMA uses ultra-high-frequency (UHF) in the 800-MHz and 1.9-GHz bands. 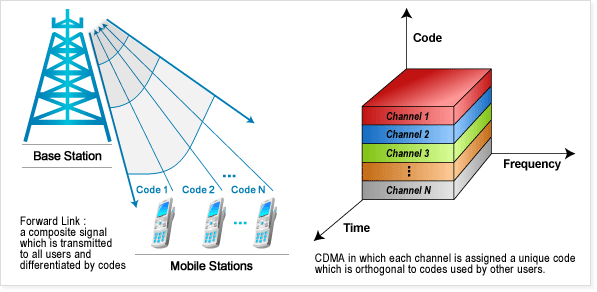
- CDMA employs analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) in combination with spread spectrum technology. Audio input is first digitized into binary elements. The frequency of the transmitted signal is then made to vary according to a defined pattern, so it can be intercepted only by a receiver whose frequency response is programmed with the same code. There are trillions of possible frequency-sequencing codes, which enhances privacy and makes cloning difficult.
GSM (Global System for Mobile communication)
A digital mobile telephony system using a variation of time division multiple access (TDMA). GSM digitizes and compresses data, then sends it down a channel with two other streams of user data, each in its own time slot. GSM is the most widely used of the three digital wireless telephony technologies (TDMA, GSM, and CDMA). It operates at either the 900 MHz or 1800 MHz frequency band.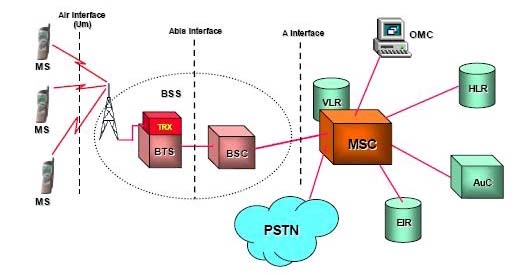
As many GSM network operators have roaming agreements with foreign operators, users can often continue to use their mobile phones when they travel to other countries. SIM cards (Subscriber Identity Module) holding home network access configurations may be switched to those that will metered local access, significantly reducing roaming costs while experiencing no reductions in service.
General Packet Radio Services (GPRS)
A packet-based wireless communication service providing connection to the Internet for mobile phones and computers from 56K to 114 K data rates. GPRS is based on Global System for Mobile (GSM) communication. GPRS packet-based services cost users less than circuit-switched services since communication channels are being used on a shared-use, as-packets-are-needed basis rather than dedicated to only one user at a time. 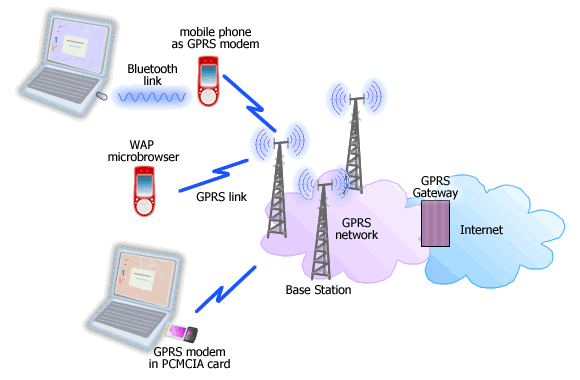
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64