Frequency
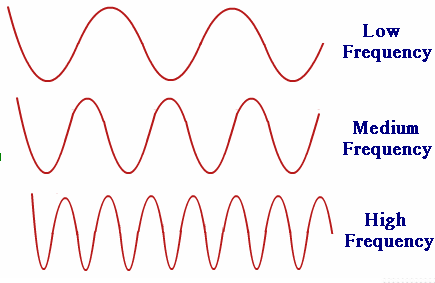
- If the signal vibrates very slowly, it has a low frequency.
- If the signal vibrates very quickly, it has a high frequency.
- Frequency is measured in Hertz, ( how fast a signal changes every second.
- FM radio signals vibrate about 100 million times per second i(high frequency)
Megahertz (MHz) and Gigahertz (GHz).
1 million vibrations a second is 1 Megahertz (MHz)
1 billion vibrations a second is Gigahertz (GHz).
1000 Megahertz is one Gigahertz.
Example Frequency Ranges
AM, FM and Television Broadcast < 1000 MHz
Wi-Fi uses 2.4Ghz and 5GHz.
Mobile phones use many different frequencies.
Frequency Modulation
A wireless signal needs to be modulated--or changed--to send information.
As the energy of the input signal is low a carrier is used to send the signal.
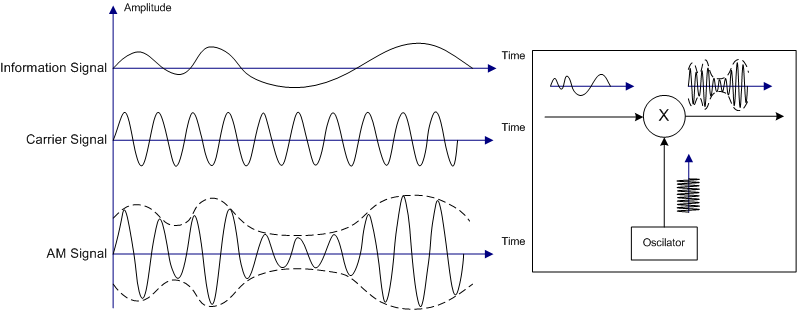
Amplitude Modulation
operate at a single frequency and modulate the energy or strength of the signal.
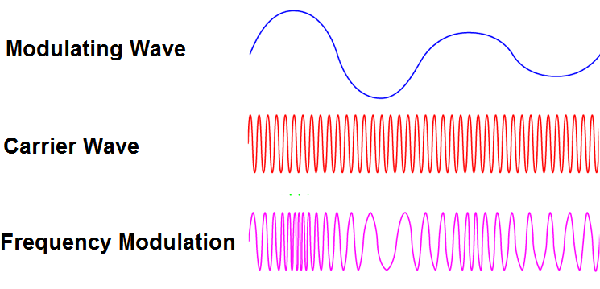
Frequency Modulation
operates at a single amplitude and modulates how quickly the wave vibrates every second
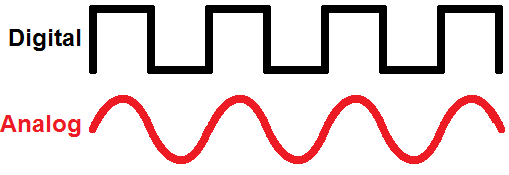
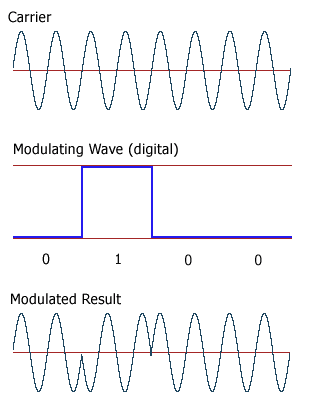
Digital and Analog Signals
Digital Modulation
PSK (phase-shift keying): a finite number of phases are used.
FSK (frequency-shift keying): a finite number of frequencies are used.
ASK (amplitude-shift keying): a finite number of amplitudes are used.
QAM (quadrature amplitude modulation): two phases and two amplitudes are used.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64