The RAM cannot cope up with increased clock frequencies and the increasing number of transistors in processor. Cache Memory is intermediate storage of high-speed RAM kept between processor and RAM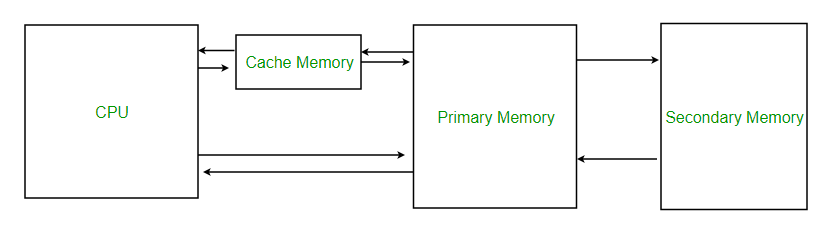
They work as buffers for data.
The cache delivers its data to the CPU registers.
The CPU can move data in different-sized packets, such as bytes (8 bits), words (16 bits), dwords (32 bits) or blocks (larger groups of bits), and this often involves the registers. The different data packets are constantly moving back and forth:
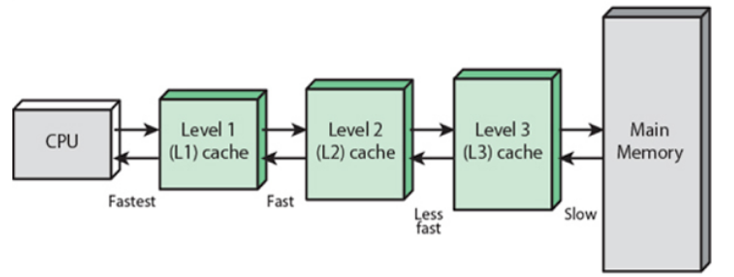
from the CPU registers to the Level 1 cache.
from the L1 cache to the registers.
from one register to another
from L1 cache to L2 cache, and so on…
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64