Carbon is a nonmetallic chemical element atomic number 6. Carbon is tetravalent, meaning it makes four bonds to other atoms. Carbon has four valence electrons, which means it has four electrons in the outermost shell to form covalent chemical bonds.


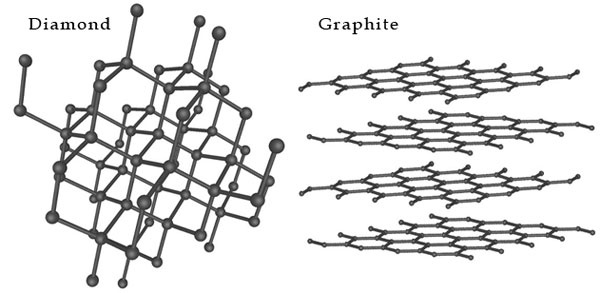
There are three natural isotopes. 12C and 13C are stable, while 14C is radioactive, decaying with a half-life of about 5730 years. There are several allotropes of carbon known as graphite, diamond, and amorphous carbon. The physical properties of carbon vary widely with the allotropic form.
For example, diamond is highly transparent, while graphite is opaque and black. Diamond is among the hardest materials known, while graphite is soft enough to write on paper.

Significant quantities of carbon found in organic deposits of coal, peat, oil and methane clathrates. Carbon forms more compounds than any other element.
Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen.
Carbon is present in all known lifeforms. In the human body carbon is the second most abundant element by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen.
Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen.
Carbon is present in all known lifeforms. In the human body carbon is the second most abundant element by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64