 RAID is a technology that is used to increase the performance and/or reliability of data storage. The abbreviation stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. A RAID system consists of two or more disks working in parallel.
RAID is a technology that is used to increase the performance and/or reliability of data storage. The abbreviation stands for Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. A RAID system consists of two or more disks working in parallel.
Hardware RAID controllers cost more than pure software but they also offer better performance. RAID combines multiple disk drives into one logical unit where all drives in the array are interdependent.
The various RAID systems designed to increase data reliability and increase input/output performance. When multiple physical disks are set up to use RAID technology, they are said to be in a RAID array. This array distributes data across multiple disks, but the array is addressed by the operating system as one single disk.
RAID 0: striping
In a RAID 0 system, data are split up in blocks that get written across all the drives in the array at the same time, RAID 0 offers superior I/O performance. However RAID 0 is not fault-tolerant. If one disk fails, all data in the RAID 0 array are lost. It should not be used on mission-critical systems.

RAID 1: mirroring
In RAID 1, Data are stored twice by writing them to both the data disk and the mirror disk. If one disk fails, the controller uses either the data drive or the mirror drive for data recovery and continues operation. RAID 1 offers excellent read speed and a write-speed that is comparable to that of a single disk. In case a disk fails, data do not have to be rebuild, they can be copied to the replacement disk.

RAID 3
On RAID 3 systems, datablocks are striped and written in parallel on two or more drives. An additional drive stores parity information. Since parity is used, a RAID 3 stripe set can withstand a single disk failure without losing data or access to data. RAID 3 is fairly complex and resource intensive and slow.

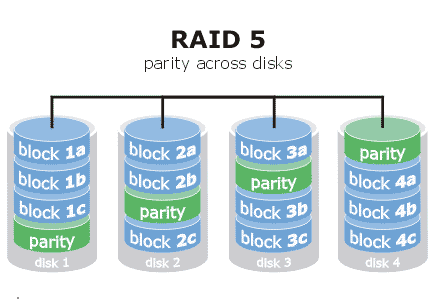
RAID 5
RAID 5 is the most common secure RAID slevel. It is similar to RAID-3 except that data are transferred to disks by independent read and write operations. The data chunks that are written are also larger. Instead of a dedicated parity disk, parity information is spread across all the drives. At least 3 disks are needed for a RAID 5 array. A RAID 5 array can withstand a single disk failure without losing data or access to data.
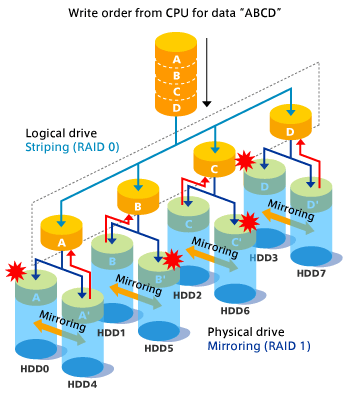
RAID 10:
RAID 10 combines the advantages of RAID 0 and RAID 1 in a single system. It provides security by mirroring all data on a secondary set of disks while using striping across each set of disks to speed up datatransfers.

Hot swapping and hot plugging are terms used to describe the functions of replacing computer system components without shutting down the system.
Once the appropriate software is installed on the computer, a user can plug and unplug the component without rebooting. Higher level RAID systems are designed for Hot swapping. In case a hard disk fail, after the hot swapping, the data in the hard disk will be re-built using parity and other disk data.
Once the appropriate software is installed on the computer, a user can plug and unplug the component without rebooting. Higher level RAID systems are designed for Hot swapping. In case a hard disk fail, after the hot swapping, the data in the hard disk will be re-built using parity and other disk data.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64