The goal of any memory device is to quickly store and retrieve data in the memory array. 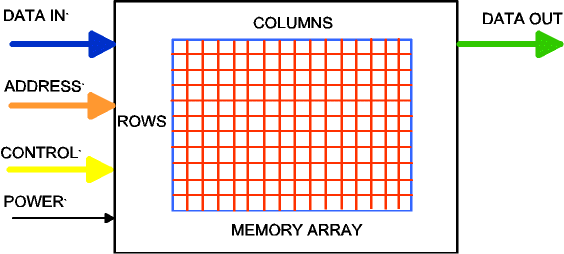
DRAM
Dynamic Random-Access Memory, is the medium that is used in personal computers and mainframes. Each DRAM component is comprised of numerous cells, or storage locations, made up of a capacitor and a transistor which can either hold an active (1) or an inactive state (0). DRAM cells are combined into a large array that is used to store vast amounts of information translated binarily by computers. 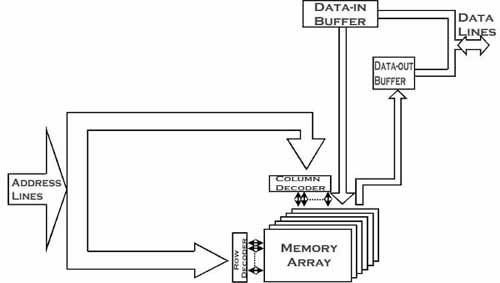
The DRAM elements are arranged in specific groups organized in terms of Rows and Columns, with each cell having a specific Row/Column reference (Address location).
SDRAM
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) were used from 1996-2002.
The memory array is composed of two banks that can be accessed independently.
SDRAM synchronizes its input and output signals with the incoming clock that is used in the system board and data transactions takes place with each successive rising edge of the clock. The system clock the main determining factor for memory operation.
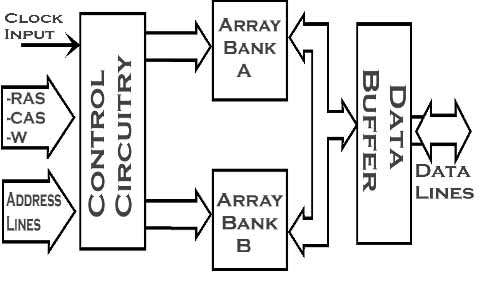
A weaness in SDRAM is that a wait state must take place before the information acquired from the memory, which makes CPU to remain idle while memory and other components in the system board catch up to its operation.
SDRAM (Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory) were used from 1996-2002.
The memory array is composed of two banks that can be accessed independently.
SDRAM synchronizes its input and output signals with the incoming clock that is used in the system board and data transactions takes place with each successive rising edge of the clock. The system clock the main determining factor for memory operation.

A weaness in SDRAM is that a wait state must take place before the information acquired from the memory, which makes CPU to remain idle while memory and other components in the system board catch up to its operation.
DDR
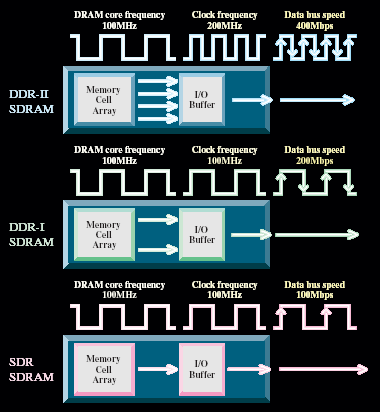
DDR stand for Double Data Rate DRAM. It is similar to SDRAM, but the transfer of data can be done at both edges of the clock signal, which allows a double rate of transmission speed. Therefore DDR is twice faster than SDRAM.
DDR2
Stand for Double Data Rate 2 DRAM is the current standard in the memory (2010). It's advatnage is the is twice speed.
Flash Memory
Flash Memory is used to quickly store data from electronic devices such as digital cameras and MP3 players. The data written to flash memory doesn't require power to maintain the stored contents. Flash memory is portable and re-writable hence has become an ideal medium for storing digital pictures and music.
Stand for Double Data Rate 2 DRAM is the current standard in the memory (2010). It's advatnage is the is twice speed.
Flash Memory
Flash Memory is used to quickly store data from electronic devices such as digital cameras and MP3 players. The data written to flash memory doesn't require power to maintain the stored contents. Flash memory is portable and re-writable hence has become an ideal medium for storing digital pictures and music.

Embedded Memory
Embedded Memory is a small, dense format frequently used on electronic devices with small form factors, such as PDAs and cell phones.
Embedded Memory is a small, dense format frequently used on electronic devices with small form factors, such as PDAs and cell phones.

Optical Memory
 In Optical Memory, data is stored on an optical medium such as CD-ROM or DVD. The data is read with a laser beam. Optical memory is an ideal solution for storing large quantities of data and transporting of data between computer devices.
In Optical Memory, data is stored on an optical medium such as CD-ROM or DVD. The data is read with a laser beam. Optical memory is an ideal solution for storing large quantities of data and transporting of data between computer devices.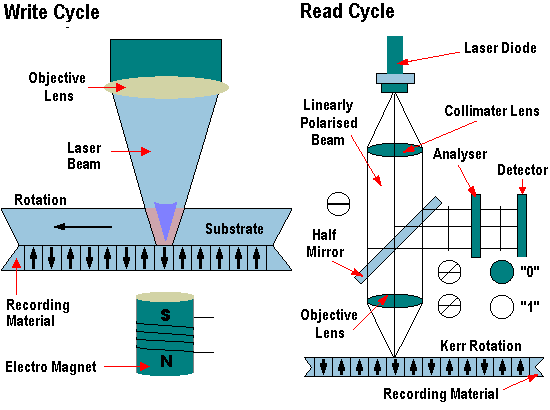
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64