Overclocking is the process of running a computer at a higher clock rate with more clock cycles per second than it was designed for. Over Clocking is done by gamers to increase the performance of their computers. 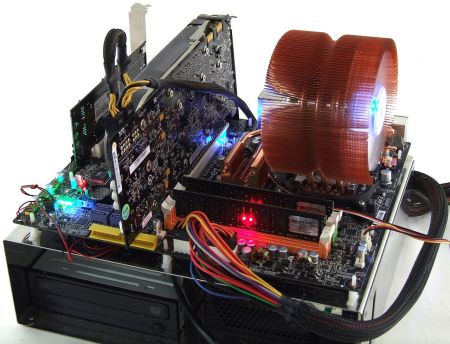
People who overclock their components mainly focus their efforts on processors, video cards, motherboard chipsets, and random-access memory (RAM). It is done through manipulating the CPU multiplier and the motherboard's front side bus (FSB) clock rate until a maximum stable operating frequency is reached.
Considerations
There are several considerations when overclocking. First is to ensure that the component is supplied with adequate power to operate at the new clock rate. However, supplying the power with improper settings or applying excessive voltage can permanently damage a component.
Cooling
All electronic circuits produce heat generated by the movement of electrical current. As clock frequencies in digital circuits and voltage applied increase, the heat generated by components running at the higher performance levels also increases.
The increased heat requires effective cooling to avoid damaging the hardware. Some digital circuits slow down at high temperatures due to changes in characteristics. Because most stock cooling systems are designed for the amount of power produced during non-overclocked use, overclockers typically turn to more effective cooling solutions, such as powerful fans, larger heatsinks, heat pipes and water cooling. Size, shape, and material all influence the ability of a heatsink to dissipate heat.
High quality heatsinks are often made of copper which has high thermal conductivity, but is expensive. Aluminium is more widely used as it is significantly cheaper than copper. Heat pipes are commonly used to improve conductivity. Many heatsinks combine two or more materials to achieve a balance between performance and cost.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64