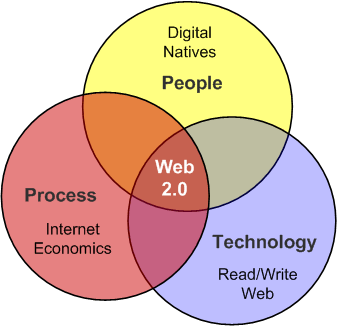
 The term Web 2.0 is associated with web applications that facilitate interactive information sharing, interoperability, user-centered design,and collaboration on the World Wide Web.
The term Web 2.0 is associated with web applications that facilitate interactive information sharing, interoperability, user-centered design,and collaboration on the World Wide Web.A Web 2.0 site gives its users the free choice to interact or collaborate with each other in a social media dialogue as creators (prosumers) of user-generated content in a virtual community, in contrast to websites where users (consumers) are limited to the passive viewing of content that was created for them. Examples of Web 2.0 include social-networking sites, blogs, wikis, video-sharing sites, hosted services, web applications, mashups and folksonomies.
Web 2.0 allows users to continue to interact with the page, communications such as data requests going to the server are separated from data coming back to the page (asynchronously). Otherwise, the user would have to routinely wait for the data to come back before they can do anything else on that page, just as a user has to wait for a page to complete the reload. This also increases overall performance of the site, as the sending of requests can complete quicker independent of blocking and queueing required to send data back to the client.
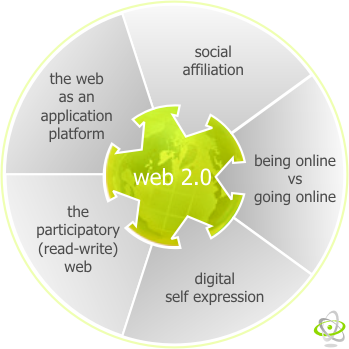
Web 2.0 draws together the capabilities of client- and server-side software, content syndication and the use of network protocols. Standards-oriented web browsers may use plug-ins and software extensions to handle the content and the user interactions.
 ශිල්ප 64
ශිල්ප 64