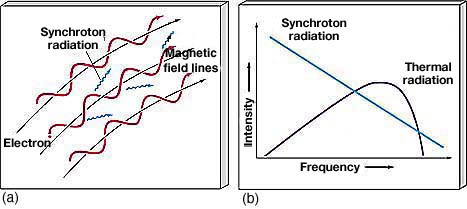
 |
Synchrotron radiation is emitted by charged particles, usually electrons, moving at relativistic speeds in magnetic fields. In a magnetic field a charged particle is forced to circle around the field line in a helical path. An accelerating charged particle emits electromagnetic radiation that is radiated along the direction in which the particle is moving. A large population of relativistic particles moving in a magnetic field will radiate over a wide range of frequencies and has a high degree of polarization. |