Units and Constants
Contents
Multiplication Factors
Common Names in SI Units
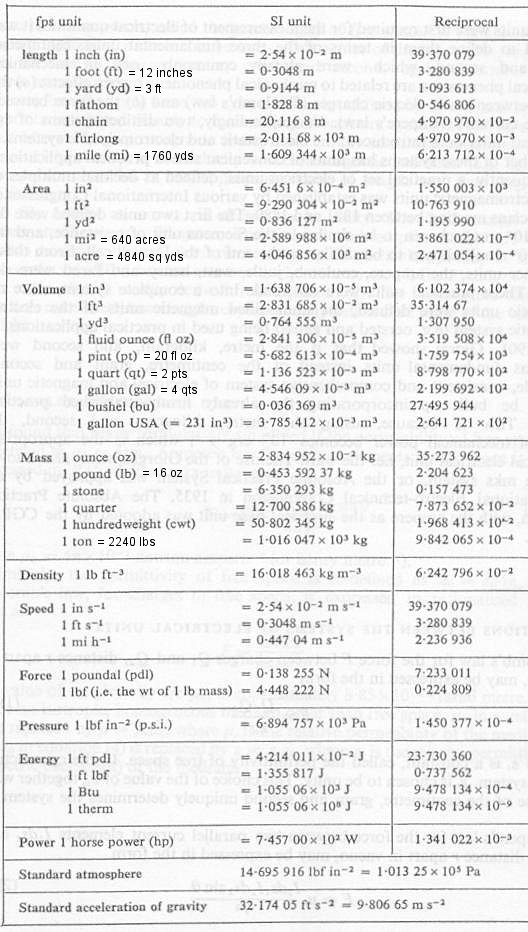
SI and British (fps) Unit Conversions
Unit Conversions
Physical Constants
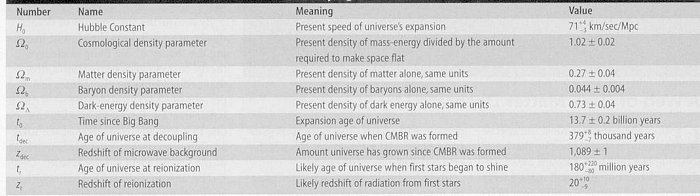
Cosmological Constants (WMAP)
Misc.
Multiplication Factors, SI Prefixes, and Symbols:

[Top]
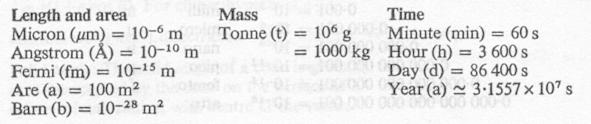
[Top]
[Top]
- 1 ly. (light year) = 1018 cm
- 1 pc. (parsec) = 3 ly. = 3x1018 cm
- 1 AU = 1.496x1013 cm
- 1 m (meter) = 100 cm
- 1 micron = 10-4 cm
- 1 ml = 1 cm3
- 1 liter = 1000 ml
- 1 knot = 1.15 mi/hr = 1.85 km/hr
- Temperature T (in oC) = T (in oK) - 273.15
- Temperature T (in oF) = 1.8 x T (in oC) + 32
- 1 ev (electron volt) = 1.602x10-12 erg
- 1 joule = 107 ergs
- 1 watt = 1 J/sec = 107 erg/sec
- 1 mi/gal = 0.354 km/liter
[Top]
- Velocity of light c = 2.998x1010 cm/sec
- Gravitational Constant G = 6.67x10-8 cm3/sec2-gm
- Hubble constant Ho = 7.1 km/sec-Mpc
- Luminosity of the Sun = 3.86x1033 erg/sec
- Mass of the Sun = 2x1033 gm
- Distance from Sun to Earth = 1 AU = 1.5x1013 cm
- Flight time of light from Sun to Earth = 499 sec
- Solar constant = 1.388x106 erg/cm2-sec
- Diameter of the Earth = 1.3x109 cm
- Mass of the Earth = 6x1027 gm
- Mean radius of the Earth = 6371 km
- Standard acceleration of gravity = 980.6 cm/sec2
- 1o of latitude = 110.5 km (at equator) = 111.7 km (at poles)
- 1o of longitude at equator = 111.3 km
- Planck's constant = 6.625x10-27 erg-sec = 4.136x10-15 ev-sec
- Avogadro's number = 6.023x1023 molecules/mole
- Normal volume of pergect gas = 2.241x104 cm3/mole
- kT = 0.0258 ev at T = 300oK
- Gas constant = 8.314x107 erg/Ko-mole
- Boltzmann constant = 1.38x10-16 erg/Ko
- Speed of sound = 34000 cm/sec
- Electronic charge = 1.602x10-19 coul
- Fine-structure constant = 1/137
- Bohr radius = 5.29 nm
- Mass of unit atomic weight = 1.6603x10-24 gm
- Nucleon rest mass = 1.67x10-24 gm
- Electron rest mass = 9.109x10-28 gm
[Top]
Critical Density = 3H02/8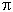 G = 10-29 gm/cm3
G = 10-29 gm/cm3
[Top]
- mega = 106, million = 106, billion = 109.
- Astronomical symbols:

- Nomenclature of Binary Molecules (compounds of only two elements, e.g., H2O, HCl) :
- For covalent molecules, element to the left and below in the periodic table (see Figure 12-19) is named first. For example, in HCl hydrogen is named first, and in BrCl bromine is named first. For ionic molecules, cation (positively charged element) is named first.
- For covalent molecules, the other element is named with "-ide" ending. For example, HCl is named hydrogen chloride, and BrCl is named bromine chloride. For ionic molecules, anion (negatively charged element) is ended with "-ide".
- When two non-metals form more than one compound from each other, Greek prefixes are used. (Note: mono- is not affixed to first element of compound if there is only one atom per molecule, e.g., CO2 is carbon dioxide, not monocarbon dioxide). For example, the prefix for one=mono-, two=di-, three=tri-, four=tetra-, five=penta-, six=hexa-, seven=hepta-, eight=octa-, nine=nona-, and ten=deca-. Therefore, the names for the following compounds are: NO - nitrogen monoxide, N2O - dinitrogen monooxide, NO2 - nitrogen dioxide, N2O3 - dinitrogen trioxide, N2O4 - dinitrogen tetroxide, N2O5 - dinitrogen pentoxide, PCl5 - phosphorus pentachloride, P2O5 - diphosphorus pentoxide, SF6 - sulfur hexafluoride, and Cl2O7 - dichlorine heptoxide.


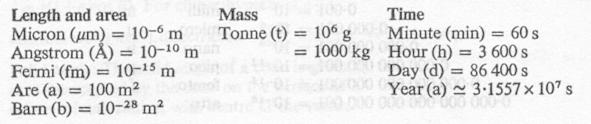
 G = 10-29 gm/cm3
G = 10-29 gm/cm3